Trip To The Future: Industry 4.0
Sarsılmaz is getting prepared for the future through Industry 4.0
There is a concept appearing very frequently before us in the recent years, bringing industry and technology together: Industry 4.0
This concept highlighted for the first time in 2012 Hannover Tradeshow
held in Germany, has been playing a central role in the progress of industry
ever since. Such approach that would be shaping the future is an inevitable
part in development of Sarsılmaz, similar to several other industrial
enterprises. Well, what does “Industry 4.0” mean and how does it contribute to
the manufacturing process? Here are certain aspects you need to know about
Industry 4.0...
As the
pioneering terms under Industry 4.0, “Industry 4.0 Platform” is described and
identified as “generation of a smart network of the machinery and processes
used in the industry with the assistance of information and communication
technology". From this perspective, Industry 4.0 means conglomeration of
digitalization with traditional industrial processes. Such process incorporates
smart chains starting from development, and leading to recycling after passing
through production, assembly, product delivery and maintenance stages,
including product lifecycles.
As a matter
of fact, in order to have a better understanding of all of the aforesaid
processes, it is worthwhile to go back a few centuries. Starting from the
second half of the 18th Century, first industrial revolution lasting nearly one
hundred years was characterized with the laying out of railways and invention
of the steam engine. This was also the beginning of the mechanical production
era.
Then the
succeeding second industrial revolution started towards the end of the 19th
Century and continued early 20th Century. The principal driving power of this
process comprised of the start-up of using electric energy as well as the assembly
line in the automotive industry by Henry Ford in 1913. Particularly in
parallel to the assembly line, employees focusing on any specific part of the
manufacturing process, brought forth serial production in conjunction.
Whereas the
third industrial revolution started in the 1960’s and reached its summit
gradually with the scientific progress towards semi-conductors, computers in
the 1960’s, followed by personal computers in the 1970’s and 1980’s and
eventually with the advent of the Internet in the 1990’s.
Thus, three
industrial revolutions preceding Industry 4.0, in other words the fourth
industrial revolution assumed essential points in history as extremely
important scientific and technological breakthroughs for mankind.
And
eventually there comes the fourth of our industrial revolutions, Industry 4.0,
in other words the era of digitalization.
Towards the Internet of objects...
As was the
case with the former industrial revolutions, fourth industrial revolution was
guided by scientific and technological developments. These developments were
led by rapidly progressing autonomous vehicle advents. Automobiles, planes,
drones or vessels arrived at a point where they could move in an autonomous
manner. In fact, the basic element underlying the same used to be inventions
regarding artificial intelligence. On the other hand, progresses in the field
of robotics and material science were amongst the factors laying ground for
Industry 4.0.
It is right
at this point that an essential concept is introduced: Internet of Things
(IOT). This concept prevails as a digital trend constituting a bridge between
physical and virtual universes. This system operating through networks
in-between things and with machinery over the Internet, enables emergence of
new business models. To this end, sensors and such other similar devices are
used to connect things with virtual networks. In short, smart systems underlie
in the background of digital production.
Our data
are increasing in magnitude when sensors, robots and artificial intelligence
are introduced, and so do the data requiring to be stored and saved. Data
generated in micro seconds on a mili-line, calculations to be made by using the
same and decisions to be adopted are referred to as BIG DATA. When it comes to
so many data, communications, calculations, it is at the same time under
development fast data processors, transmitters, algorithms and memories for
saving and using these data.
What is of
critical essence at this point is proper analysis of the term “smart”. The
concept of “smart” referring to a system of machinery connected to a network
and capable of interacting creates added value for the users. To this effect,
it could be referred to three different trends in terms of terminology; smart
factories, smart products and smart services.
What does a smart factory mean?
The
expression “smart factory” basically means such adaptable manufacturing systems
connected to one another via software as well as to networks generating added
value at varying levels. Beyond all, operators make avail of rapid
dissemination and utilization of data. In order to ensure the most reliable or
predictable data exchange between equipment and services, network and real-time
communication, scalability is yet another factor bringing forth success. On basis
of decentralized intellect, such scalable architectures are able to make their own
decisions.
Smart
factories are structures based on data, analysis and systems with the capacity
to act by basing on such analysis. To the effect, data mining, data analysis
and efficient operations conducted connected to automation as a result of such
data analysis prevail.
Smart
factories are positioned at the heart of Industry 4.0. The purpose is to create
an autonomous manufacturing process where men, machinery, facilities and
products communicate with one another independently. Cyber-physical systems
make production more flexible. This feature also creates a leading edge
regarding applicability of customer demands through data processing.
Subject
matters systems become functional upon consecutive lining of the following
layers.
- Business
(Organization and business processes)
-
Functioning (Functioning of embedded element sor other components)
-
Information (Necessary data)
- Communication
(Access to data)
- Integration
(Transition from physical to the digital world)
- Presence
(Real object in the physical world)
These
layers (strata) are applied in each and every stage of the production
activities in any factory ranging from the incoming raw material to the
outgoing finished product, thereby arriving at the result.
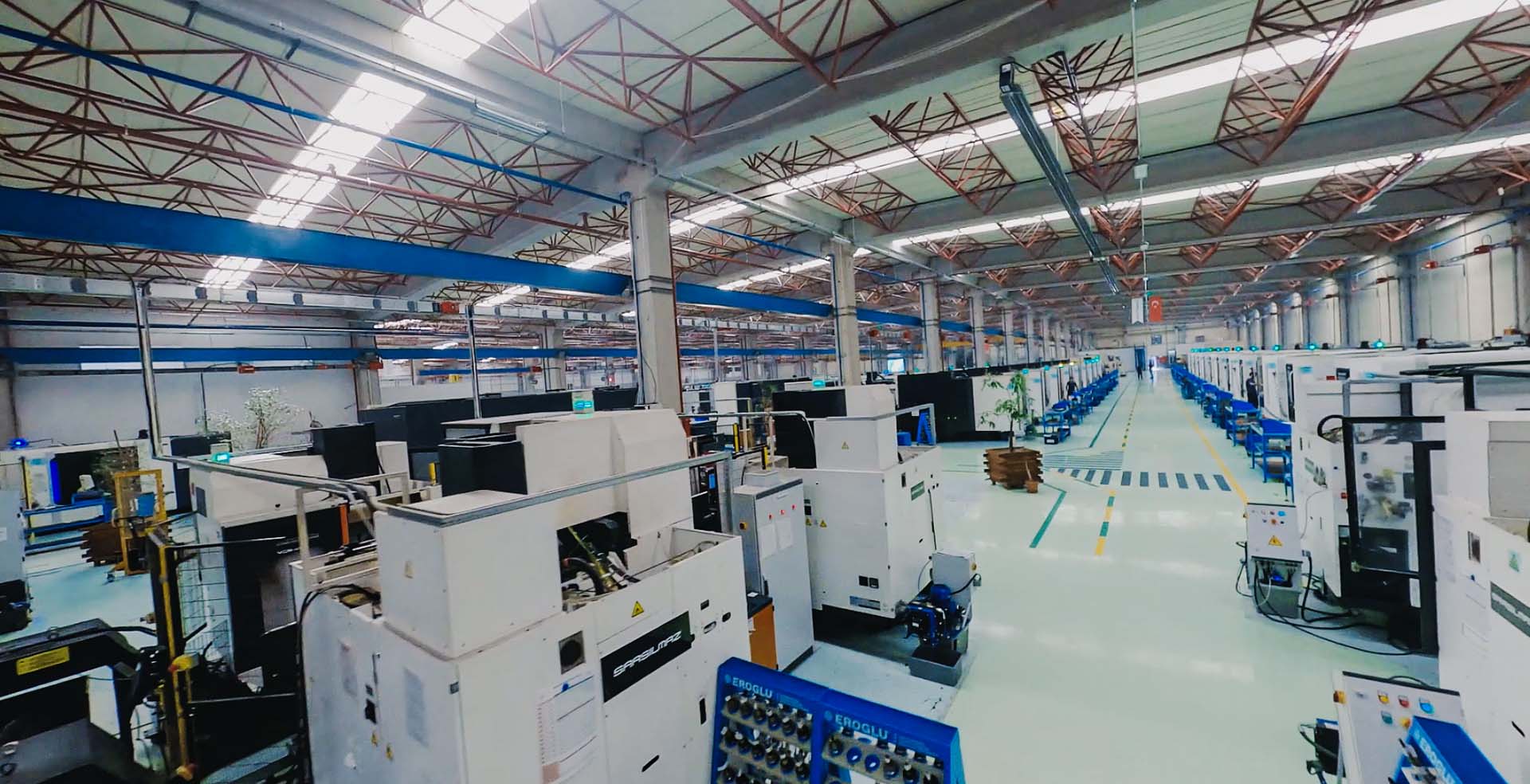
Sarsılmaz is getting prepared for Industry 4.0
As the
innovative and creative segment of any current technology in the field of
industry is doubtlessly an inevitable objective for Sarsılmaz as well,
requiring due implementation. Within framework of superstructure R&D activities,
while Sarsılmaz is stepping ahead with essential steps regarding product
development, is on the other hand involved in an intensive activity to convert
its production facilities into smart premises.
The main
target at this point comprises of bringing together an effective organization
structure with correct production elements. It is of crucial essence to merge
data as our contemporary major asset with a systematic process that is
renewable at all times, creating an autonomous infrastructure processing these
data, transferring to the digital domain both the feedback data coming from the
customers as well as data derived from scientific advances and thus creating
the perfect product via autonomous structures making up such a system.
Future is shaped by Industry 4.0, yet Industry 4.0 itself is incessantly improved and renewed depending on the technological and scientific innovations. From this viewpoint, it is required to avoid losing time in adapting to Industry 4.0, because we are faced with an ever transforming structure.
 CLOSE
CLOSE
 Sarsılmaz At A Glance
Sarsılmaz At A Glance